Refrigerant(g)
Refrigerant are working substances that form freezing cycle; in their liquid state, they absorb heat from surrounding materials and evaporate at low temperatures, cooling the materials.
In 1928, General Motors (GM) in the United States first developed Freon 12 (chlorofluorocarbon). In 1930, they began production in collaboration with DuPont under the trademark "Freon." Because Freon is extremely stable chemically and thermally, it was hailed as a dream chemical when it was first developed.
The refrigerant of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) led to dramatic advances in refrigeration technology. However, it was discovered that the chlorine refrigerant refrigerant CFCs, HCFCs) R12 and R22 reaches the Earth's stratosphere and destroys the ozone layer, which blocks ultraviolet rays from penetrating the atmosphere. As a result, their production and use was completely banned (1995). Furthermore, chlorine-free HFCs are also contributing to global warming, so their use is being reconsidered. Currently, research and development of alternatives to fluorocarbon refrigerant is underway in the field of refrigeration technology. These alternatives include isobutane and carbon dioxide (CO 2), collectively known as natural refrigerant, and are attracting attention.
Control panel cooling unit and other appliances use R134a and R407C (a three-type mixed refrigerant), which are known as alternative refrigerants. From the perspective of global environment conservation, there are restrictions on the use and disposal of HFCs and mixed refrigerant, and disposal without permission is subject to administrative sanctions (Fluorocarbons Recovery and Destruction Act and Fluorocarbons Emissions and Proper Management Act).
Reference link → Fluorocarbon Emissions Control Law
Comparison of ozone depletion and global warming potential of various refrigerant
| Kinds | symbol | Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) |
global global warming potential (GWP) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFC | Chlorofluorocarbons | R-12 | 1 | 10900 |
| HCFC | Hydrochlorofluorocarbons | R-22 | 0.055 | 1810 |
| HFC | Hydrofluorocarbon-1 | R-134a | 0 | 1430 |
| Hydrofluorocarbon-② | R-32 | 0 | 650 | |
| HFC mixture | Hydrofluorocarbons 3 types (2 types) mixed refrigerant |
R-407C | 0 | 1774 |
| R-410A | 0 | 1980 | ||
| R-404A | 0 | 3780 | ||
| HFO | Hydrofluoroolefin | R-1234yf | 0 | 4 |
| natural refrigerant | Isobutane and carbon dioxide (CO 2) | R-600a | 0 | 3 |
| R-744 | 0 | 1 | ||
refrigerant designations
| Single refrigerant | Azeotropic refrigerant mixture | Non-azeotropic refrigerant mixture | Inorganic refrigerant |
|---|---|---|---|
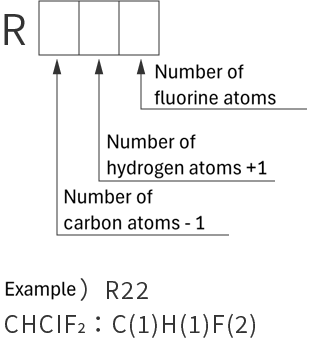 |
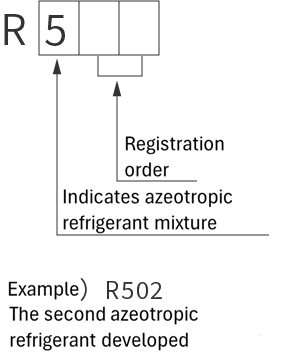 |
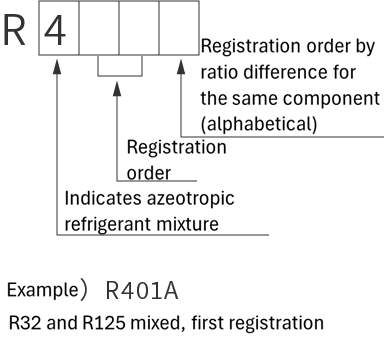 |
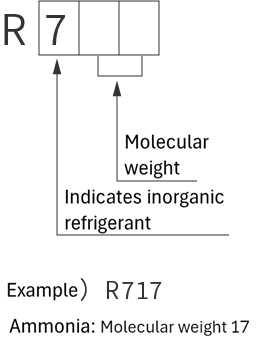 |
*Azeotropic means that the boiling points of the mixed refrigerant are almost the same. Non-azeotropic means that the boiling points of the mixed refrigerant are different.






