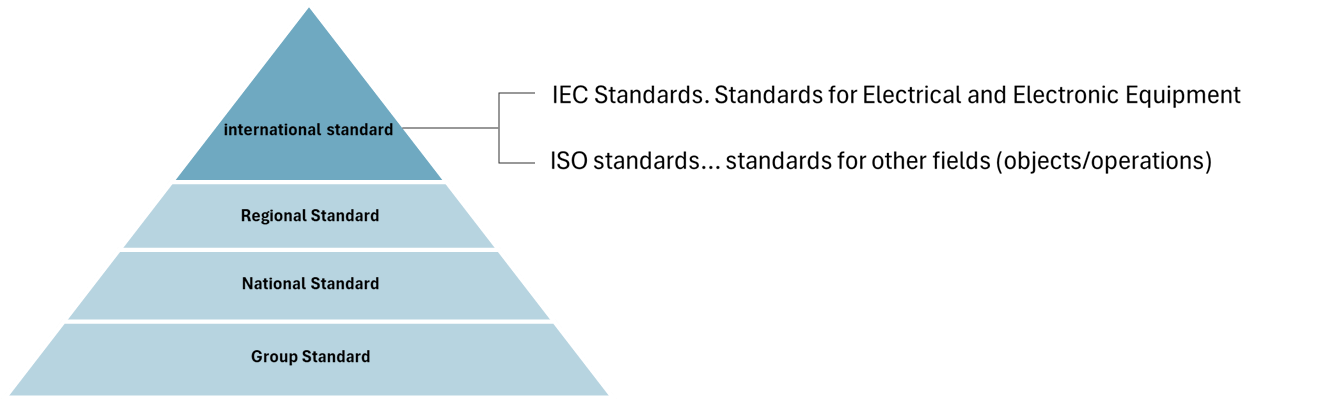
International Standards
IEC standard
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) is an international standardization organization founded in 1908 that specializes in electrical and electronic technology and related technical fields. Its technical committees and subcommittees work in collaboration with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) to plan and develop international standards (IEC standards) such as Directives, standards conformance (ISO/IEC17000 series), and information technology (ISO/IEC/JTC1) to ensure the quality and safety of products that comply with those standards.
IEC Homepage
https://www.iec.ch/
ISO standard
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is a non-profit organization headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. Founded in 1947, it develops international standards (IS). It is an independent organization whose mission is to promote global mutual assistance in international standards. It promotes global trade by providing common standards between countries. Its approximately 20,000 standards cover all fields, including industrial products, technology, food safety, agriculture, and medicine. Using ISO standards helps create safety, reliable, and high-quality products and services, minimize defects, and improve productivity. ISO standards protection consumers and end users of products and services and ensure that products conform to minimum internationally established standards.
ISOホームページ
https://www.iso.org/iso/home.html
International Standards System
Europe (Europe)
EN Standards
EN standards are unified European standards issued by CEN (European Committee for Standardization), CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization), and ETS (European Telecommunications Standards Association), which are made up of 30 European countries. Member countries are required to adopt EN standards as their national standards. They are also called CEN standards (CEN/CENELEC standards) or European standards.
CENELEC (Electrical Sector) Homepage
https://www.cenelec.eu/
CEN (Non-Electrical Fields) Homepage
https://www.cen.eu/Pages/default.aspx
CE marking
CE marking is a mark that display that products sold (put on the market) in the EU (European Union) comply with EU standards. CE marking indicates that the product complies with the essential requirements set out in sector-specific EU directives and regulations. "CE" is an abbreviation of the French word "Conformite Europeenne" (English: European Conformity).
Most of the essential requirements relate to product safety, but in recent years, CE marking has become a requirement to declare that a product complies with the environment performance standards set out in the RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) Directive and the Ecodesign Directive. The manufacturer (importer) of the product in question, or a third-party certification body acting on their behalf, conducts the required conformity assessment and affixes the marking to the product, packaging, and accompanying documentation. Products with the correct CE marking are guaranteed to be freely sold and distributed within the EU.

New Approaches Directive
The New Approach Directives, which aimed to eliminate technical trade barriers, were adopted in 1985 with the aim of harmonizing product standards, safety regulations, and other rules in line with the movement toward unification of economic markets. Directives such as the 1) Machinery Directive, 2) Low Voltage Directive, and 3) EMC Directive were established for each specific product characteristic, specifying the standards (essential requirements) that each product must comply with, and EN standards (EU unified standards) that embody these standards were established as harmonized standards.
Machinery Directive: 2006/42/EC
This is a safety standard for machines that operate on electricity, pneumatics, hydraulics, etc. as energy, and is a directive on the safety of machinery and safety components used to prevent accidents caused by machines (mechanical safety). The manufacturer or agent is required to go through the conformity assessment procedure.
Health safety Fulfillment of requirements, preparation of technical documentation, certification by a notified body as required, preparation of EC declaration of conformity, affixing of CE marking, etc. are mandatory. In addition, the penalties that apply to violations of the directive are stipulated in the national laws of each country.
Machinery Directive details
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32006L0042
Low Voltage Directive: 2014/35/EU
The main purpose of this directive is to ensure safety free circulation of electrical products within the EU while ensuring safety safety of electrical equipment. With the exception of specific exemptions, it applies to electrical equipment designed to be used within the voltage range of 50 to 1000V AC or 75 to 1500V DC. Specific requirements are stipulated for each standard, but the following outline of technical requirements is generally required.
1) People cannot approach dangerous areas (areas where dangerous voltages are applied, moving parts, etc.)
2) The temperature of parts that can be touched by people will not become so high that it poses a risk of burns.
3) The temperature of each part will not become so high that it poses a risk of fire or insulation deterioration.
4) No dangerous radiation (laser, electromagnetic waves, radioactive rays, etc.)
5) The housing is strong enough
6) No risk of tipping over under foreseeable conditions of use
7) Proper insulation
8) protection earthing (if required) is appropriate
9) No risk of fire
10) Leakage current is not too large
11) safety is not compromised even under single fault conditions
12) All necessary display are properly displayed.
13) The instructions in the instruction manual are properly written
Details of the Low Voltage Directive
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32014L0035
EMC Directive: 2014/30/EU
EMC stands for Electro Magnetic Compatibility. Its purpose is to prevent electromagnetic interference and it defines two main protection requirements.
1) The electromagnetic interference generated by the equipment is radio/
Do not interfere with the operation of communications equipment or other devices (emissions)
2) No unacceptable performance degradation in the intended environment
Electromagnetic interference immunity to ensure operation
In order for the target devices to be distributed, they must satisfy these protection requirements.
A distinctive feature of the EMC Directive is that it applies to the majority of electrical and electronic devices sold. Another major feature of this directive is that it regulates both emissions and immunity, whereas other regulations, such as Japan's Electrical Appliance and Material safety Act and VCCI regulations, and the United States' FCC regulations, primarily regulate emissions. Applicability of industrial products is primarily determined using the immunity (EMS: Electromagnetic Susceptibility) standard EN61000-6-2 and the emission (EMI: Electromagnetic Interference) standard EN61000-6-4.
Details of the EMC Directive
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32014L0030
RoHS Directive: 2011/65/EU
This is a European law that restricts the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment. It was amended by Directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of June 8, 2011. The revised RoHS Directive restricts the inclusion of 10 substances in all electrical and electronic equipment (excluding exempted products) with rated voltage of AC 1000V / DC 1500V or less that are placed on the EU market. Of the four phthalate substances that were newly added in June 2015, DEHP is a substance commonly used in Japan for electrical wire coatings and as a plasticizer for plastics, and replacement is expected to accelerate in the future.
<Controlled substances>
・Lead (lead and its compounds): 1000 ppm or less
- Mercury (mercury and its compounds): 1000 ppm or less
・Cadmium (cadmium and its compounds): 100 ppm or less
- Hexavalent chromium (hexavalent chromium and its compounds): 1000 ppm or less
- Polybrominated biphenyls (PBB): 1000 ppm or less
- Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE): 1000 ppm or less
・Diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP): 1000 ppm or less
-Butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP): 1000 ppm or less
- Dibutyl phthalate (DBP): 1000 ppm or less
- Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP): 1000 ppm or less
Details of the RoHS Directive
https://ec.europa.eu/environment/topics/waste-andrecycling/rohs-directive_en
North America
UL standard/CSA standard
North American (including Canadian) regulations for electrical products require imported products to be certified by a third-party accredited testing laboratory in the country of origin. Testing laboratories certified by the Occupational safety & Health Administration (OSHA) are called Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratories (NRTL).
Several companies are certified, including safety Laboratories (UL), Intertek Testing Services NA, Inc. (ITSNA, formerly ETL), and the Canadian Standards Association (CSA). Certified products are permitted to affix a certification label, which is display in accordance with display items and display specified by each certification body.
The United States and Canada have concluded a Mutual Recognition Agreement (MRA) that enables mutual recognition.
UL standards include "listing marks" that are affixed to finished products, etc., and "recognition marks" that are affixed to parts that function by being attached to something else.

People's Republic of China
China Compulsory Certification System (CCC System)
The CCC (China Compulsory Certification) system was established in 2002 when China joined the WTO in 2001 to consolidate the various certification systems that existed in the country and align the Chinese national standards (GB standards), which serve as the technical standards for the CCC certification system, with international standards such as IEC and ISO.
The CCC system is based on the Compulsory Product Certification Administration Regulations issued by the General Administration of weight Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China (AQSIQ) and the Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People's Republic of China (CNCA). For the purposes of protection national safety, preventing fraud, protection human health or safety, protection the life or health of animals and plants, and protection environment, products listed in the "Compulsory Certification Product Catalog" must pass inspection by a certification body and display a certification mark. Products cannot be shipped, sold, imported, or used in other business activities unless they display the certification mark.
<CCC subject items>
・Electric wires and cables
Circuit switches and electrical devices for protection or connection
・Low voltage generator
・Small output motor
・Power tools
・Electric welding machine
・Facilities for home and similar purposes
・Audio/video equipment
・Information technology equipment
・Lighting equipment
Vehicle and safety accessories
・Vehicle tires
・ safety glass
・Agricultural equipment
・ power supply terminal equipment
・Firefighting products
・ safety crime prevention products
・Wireless LAN products
・Decorative interior products
・Toy products
CCC Certification Details
http://www.cnca.gov.cn/

Japan
JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards)
JIS: An abbreviation for Japanese Industrial Standards, it is one of Japan's national standards. It is an industrial standard established by the Minister based on the Industrial Standardization Act and recommendations from the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. On July 1, 2019, the Industrial Standardization Act was amended to include data and services, and the name was changed from "Nihon Kogyo Kikaku" to "Nihon Sangyo Kikaku."
JIS standards are based on ISO and IEC standards as determined by an international agreement in 1955.
Japan Industrial Standards Committee website
https://www.jisc.go.jp/

PSE Standards (Electrical Appliance and Material safety Act)
PSE: An abbreviation for Product Safety Electrical & Materials, and products bearing the mark meet technical safety standards. There are two types of marks: a diamond mark for "specific electrical appliances" and a round mark for "electrical appliances other than specific electrical appliances." Products must be verified for electrical appliance safety and EM (Electron Microwave Emission) compliance, and the PSE mark must be display on the equipment.
Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry Electrical Appliance and Material safety Act page
https://www.meti.go.jp/policy/consumer/seian/denan/index.htm







