Causes of equipment shutdown
In order to increase equipment utilization rates (i.e., increase production efficiency), it is essential to first ensure that the equipment does not stop. The causes of equipment stoppages can be broadly divided into mechanical and electrical factors.
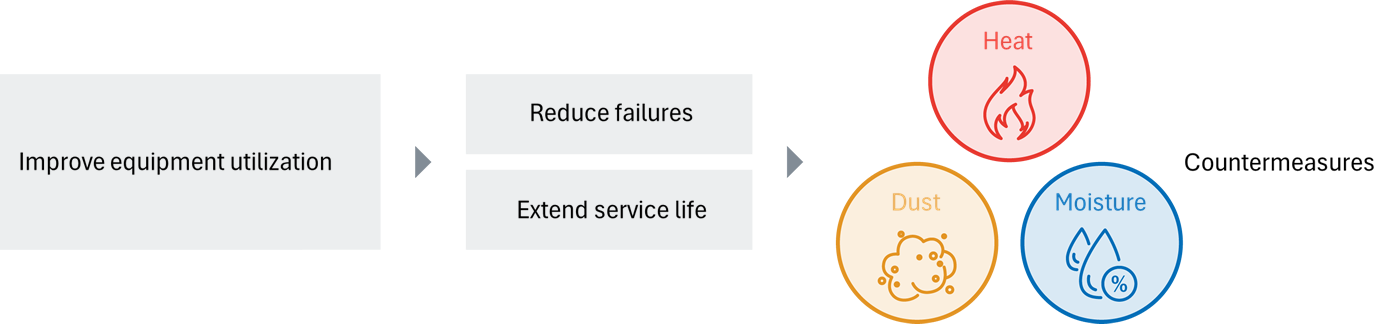
In short, the main reasons why equipment stops (= the reason why equipment operating rates do not improve) are "breakdown" and "lifespan."
Panel is the center of electrical control for a facility.
panel is a device that houses drive control devices such as inverters, servo amplifiers, transformers, and breakers, as well as power supply transformers and wiring devices, all wired and housed in a housing to control machinery and equipment as a whole according to its purpose.
Panel problems are thought to be primarily caused by heat, dust, and humidity.




In other words, to increase the operating rate without stopping equipment...
The following are considered important:

Learn the basics of heat problems and how to solve them!
A 24-page resource focusing on thermal issues in panel.
Heat-related problems in panel and how to solve them
We will introduce you to the following.
Causes of heat generation in panel and how to calculate the amount of heat generated
When power supply turn on an electrical device, the device generates heat.
Within panel, control devices such as inverters and servo amplifiers are not only used frequently, but also generate a lot of heat, raising concerns about deterioration and failure due to heat.
It is known that energy ultimately becomes heat.
Typical examples include electrical, optical, and mechanical energy.
In reality, not all input energy is output (= consumed for work). The energy lost when converting input to output becomes heat and is generated (= heat loss).
The calorific value is calculated using the following formula:
The part in the above equation (1 - conversion efficiency) is called the heat loss ratio.
Note: Detailed heat loss ratios for control equipment are published by each manufacturer.
For an estimate of heat generation, please refer to the article "List of heat generation of equipment stored inside the panel."
Inverter heat generation
Inverters are power semiconductors that pass large currents and are therefore one of the devices that are particularly prone to generating a lot of heat.
The heat output of the inverter is also calculated using the above formula.
If the conversion efficiency of a typical inverter is 95%, then if rating is 7.5kW,
7.5kW x (1 - 0.95) = 0.375kW (= 375W).
This heat loss causes heat generation inside panel.
The heat loss ratio varies depending on the equipment and rating output, but generally the smaller the rating output, the larger the heat loss ratio, and the larger the rating output, the smaller the heat loss ratio.
The heat output for each rating output is based on the guidelines for equipment stored in panels issued by the Panel Heat-Related Equipment Industry Association.
It can be calculated based on the estimated heat output.
*The heat output of the inverter decreases as the load and usage rate decrease, so the exact heat output must be calculated according to the manufacturer's specification.
| Equipment stored inside the panel | Heat output (general guideline) | |
|---|---|---|
| AC servo amplifier | rating Output ~0.1kVA about 40% ~0.5kVA approx. 10% ~1kVA about 8% ~3kVA about 5% |
~5kVA approx. 4% ~11kVA about 3.5% ~22kVA about 3% |
| inverter | rating Output ~0.4kW approx. 12.5% ~0.75kW approx. 11% ~1.5kW approx. 8% ~2.2kW approx. 7% ~3.7kW approximately 6% |
~7.5kW approx. 6% ~11kW about 5% ~22kW approx. 4.5% ~30kW around 4% |
Please refer here for a guide to the heat generation of equipment stored inside the panel.
→List of heat generation from equipment stored inside the panel


