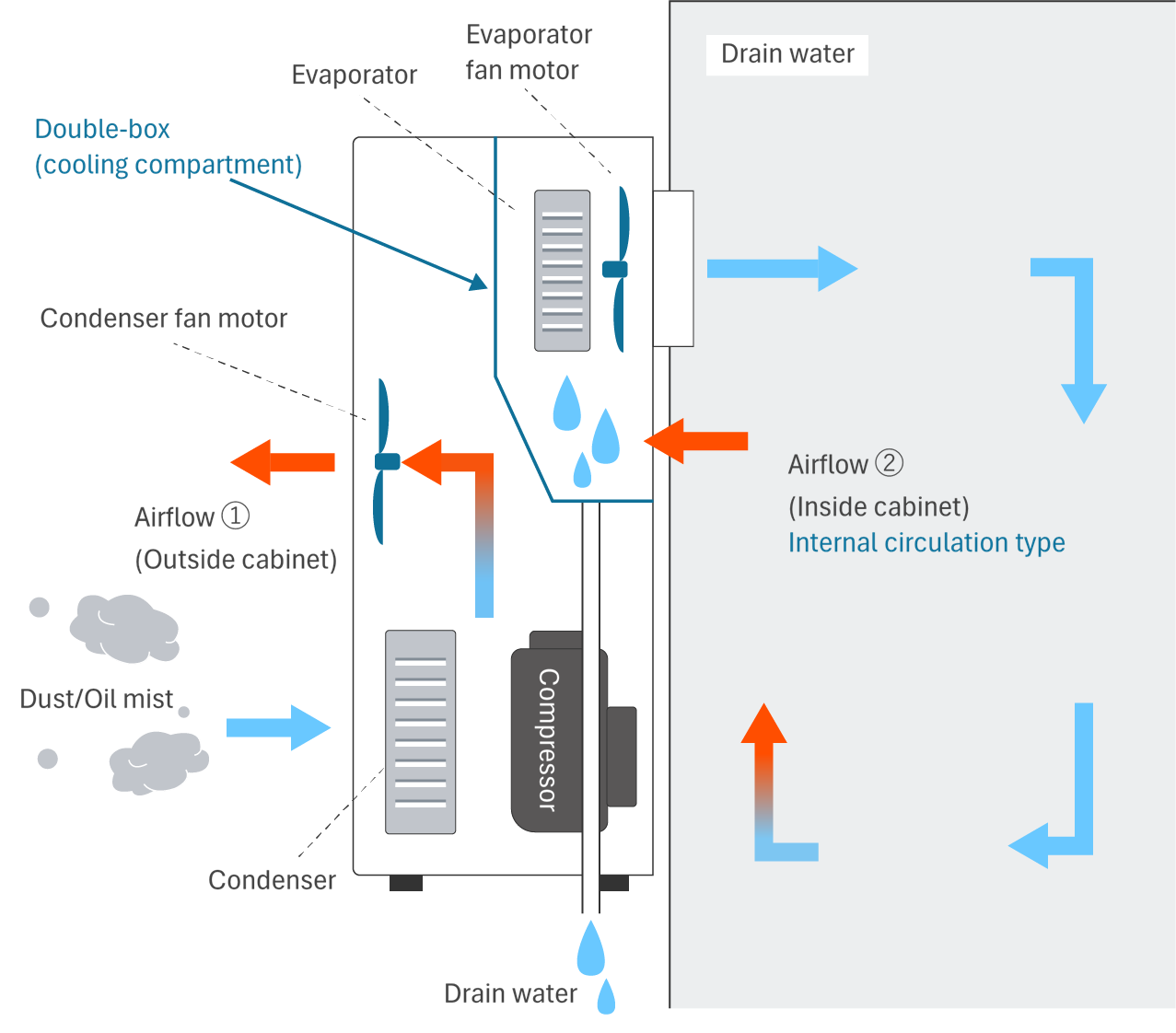
"Internal circulation type double box structure" for dustproof construction

The structure of our control panel cooling unit is, Internal circulatory structure Also, Double box structure The first two are the following.
Therefore, even environment with dust and oil mist, dirty air is not drawn into the board and the inside of the board can be kept clean.
Point 1: There are two systems of wind flow on control panel cooling unit: "inside the board" and "outside the board".
Point 2: There is a sealed double box (cooling room) inside control panel cooling unit that is independent of the outside of the board.
Point 3: Dirty air on the outside heat dissipation side of the board is, No intrusion into the board. The following is a list of the most common problems with the "C" in the "C" column.
Point 4: For this reason, Circulation path in the board is equivalent to IP54 It is. * Excluding the drain pipe section
Side mounting type

Use a control panel cooling unit to make the internal board environment the best condition it can be!
control panel cooling unit protect electronic devices inside panel from heat, dust, and humidity, contributing to the stable operation of production lines.
Please check the catalog for the latest lineup, functions and features.
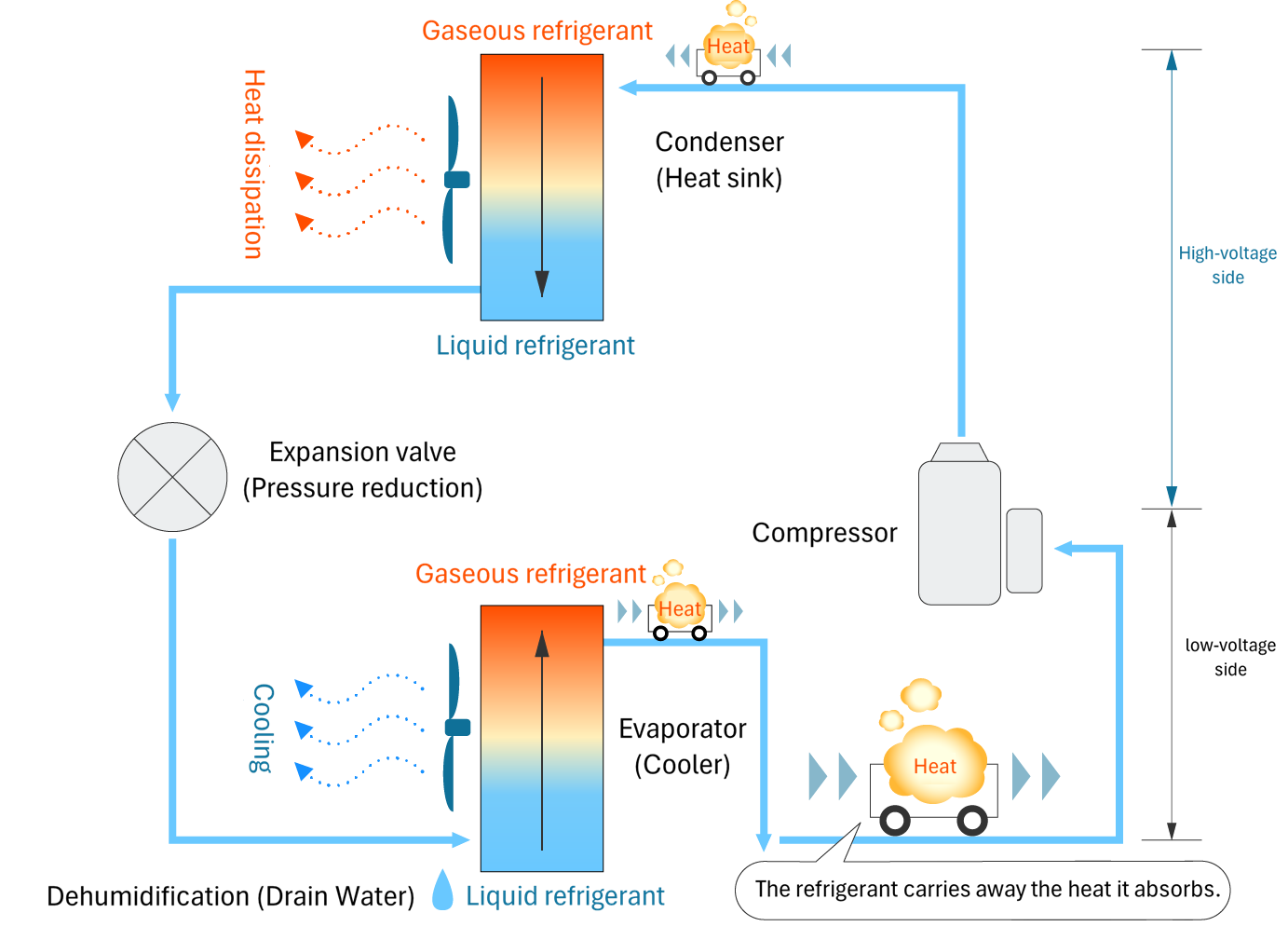
Equipped with freezing cycle for cooling and dehumidification


control panel cooling unit has a compact structure in which the indoor and outdoor units of a room air conditioner are integrated.
The outdoor unit is the condenser, and the indoor unit is the evaporator.
condenser The heat was absorbed outside the board. Releases heat So "Radiator" It is also called.
This refers to the outdoor unit side that blows out warm air.
evaporator is in the board absorbs heat This causes the temperature to drop and cool down "Cooler" This refers to the indoor unit of the air conditioner that blows cool air.
The condenser and evaporator heat exchanger This utilizes the property of heat moving from high to low temperatures.
In freezing cycle, the important role is refrigerant refrigerant is The role of transporting heat We are doing this.
freezing cycle is illustrated below:
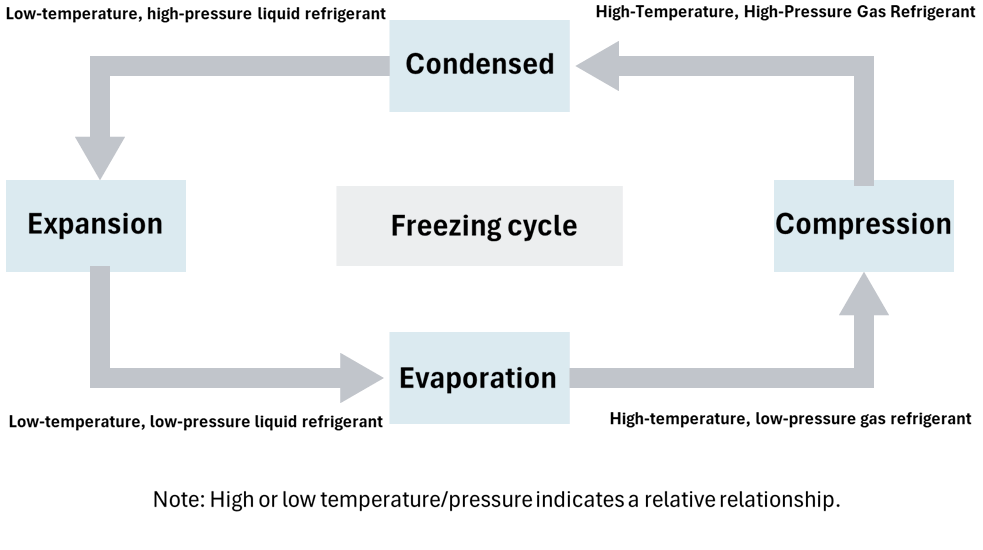
- Compression
- In order to condense and liquefy gas refrigerant using room temperature air or water, the temperature of refrigerant must be raised further, so the gas refrigerant is continuously compressed in the compressor, raising its temperature before being discharged.
- Condensation
- When high-temperature, high-pressure gas refrigerant is cooled by the surrounding air or water, it condenses and becomes a liquid, releasing the heat that was exchanged in the condenser.
- Expansion
- The high-pressure liquid refrigerant expands immediately after its flow is restricted by the expansion valve, and as some of the liquid refrigerant evaporates, it absorbs heat, lowering refrigerant 's temperature.
- Evaporation
- The low-temperature, low-pressure liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from the air it comes into contact with and evaporates. The air that absorbs the heat is cooled and sent out as cool air.
A quick explanationHeat Exchanger Efficiency and Causes of Insufficient Cooling
The cooling capacity of cooler varies depending on its heat exchange capacity.
The efficiency of a heat exchanger depends on the following factors:
①The temperature difference between the object being heat exchanged is large
②Good heat transfer (thermal conduction)
3) Large contact area for heat exchange
④Air volume for heat exchange
From the above, the reasons why cooler does not cool are
・Ambient temperature is high ⇒ The temperature difference in heat exchange decreases (①)
・ clogging filter ⇒ Heat dissipation decreases, reducing the temperature difference (①④)
・Fin contamination ⇒Thermal conduction on the fin surface deteriorates and the contact area also decreases (②③)
・Fan airflow rate decreases ⇒ heat dissipation rate decreases (④)
This means that...
To ensure efficient cooling, it is important to use the unit in a good environment and perform regular maintenance.
Apiste 's unique "mild cooling" for safe and comfortable cooling and dehumidification
control panel cooling unit can be broadly divided into two types.
・ Quick cooling cooler "rapid cooling type"
Rapid cooling type control panel cooling unit are designed to cool the inside of panel quickly.
・ Slow cooling cooler "Mild cooling type"
This is the type of control panel cooling unit that thinks that when the equipment in the cabin heats up and the temperature inside the cabin rises, it is better to cool it down slowly little by little. Apiste control panel cooling unit has made its unique mild cooling a product concept from the very beginning of its development.
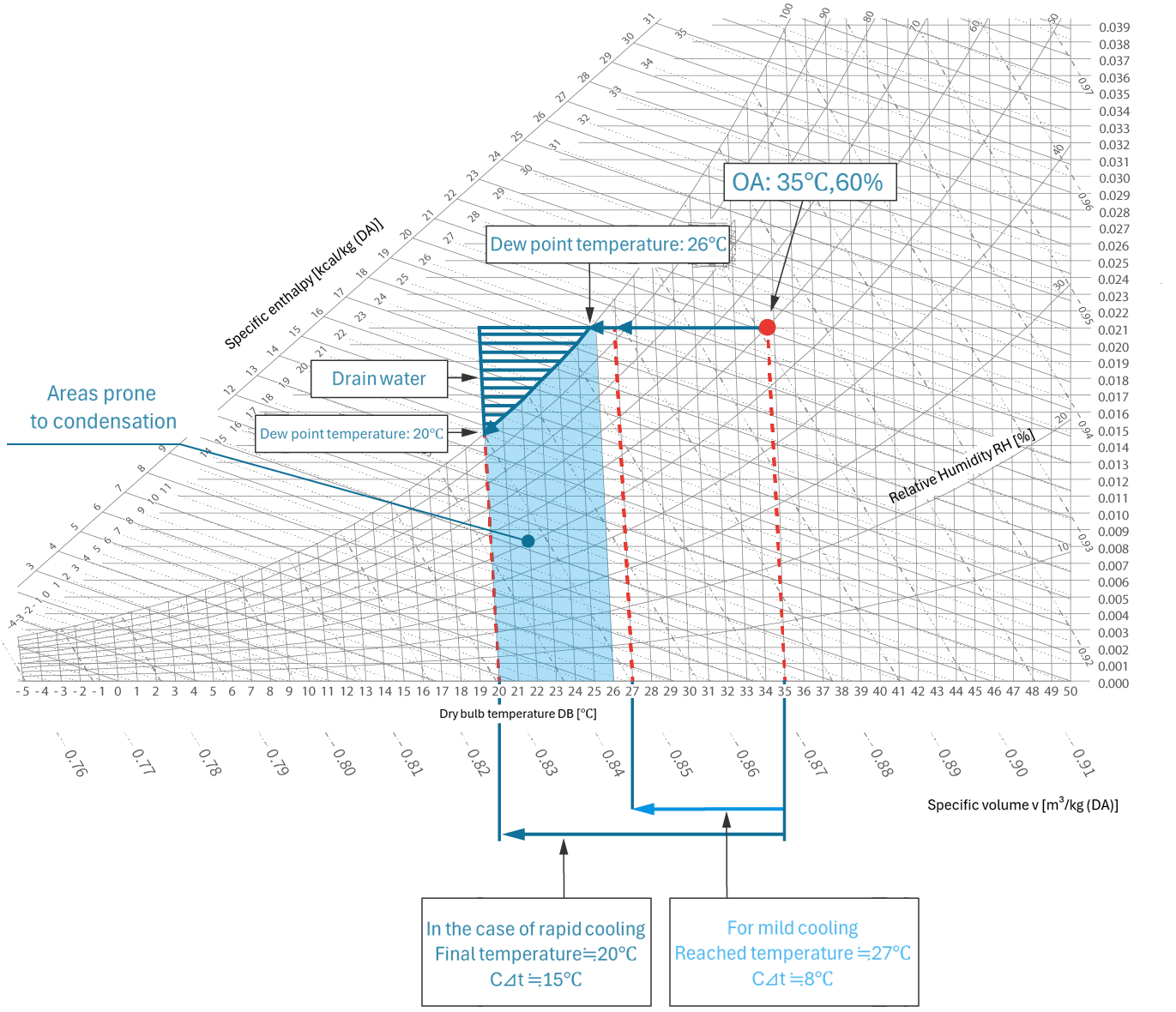
The psychrometric chart below compares the results when the temperature inside panel is 35°C/60% and cooled using ① rapid cooling (discharge temperature difference = 15°C) and ② mild cooling (discharge temperature difference = 8°C).
35°C/60% dew point temperature ≒ 26°C (there is a risk of condensation if the temperature drops below the dew point)
・Temperature reached in case of rapid cooling: ≒ 20℃
・Temperature reached in case of mild cooling: ≒ 27℃
-What are the problems with rapid cooling?
① Due to supercooling, the temperature drops below the dew point, making condensation more likely to occur.
② There is a possibility that drain water will suddenly come out.
-What are the benefits of mild cooling?
1. The dew point temperature is unlikely to be exceeded, so the risk of condensation is extremely low.
② There is a low risk of drain water suddenly coming out.
The difference between rapid cooling and mild cooling is shown in the psychrometric chart below.
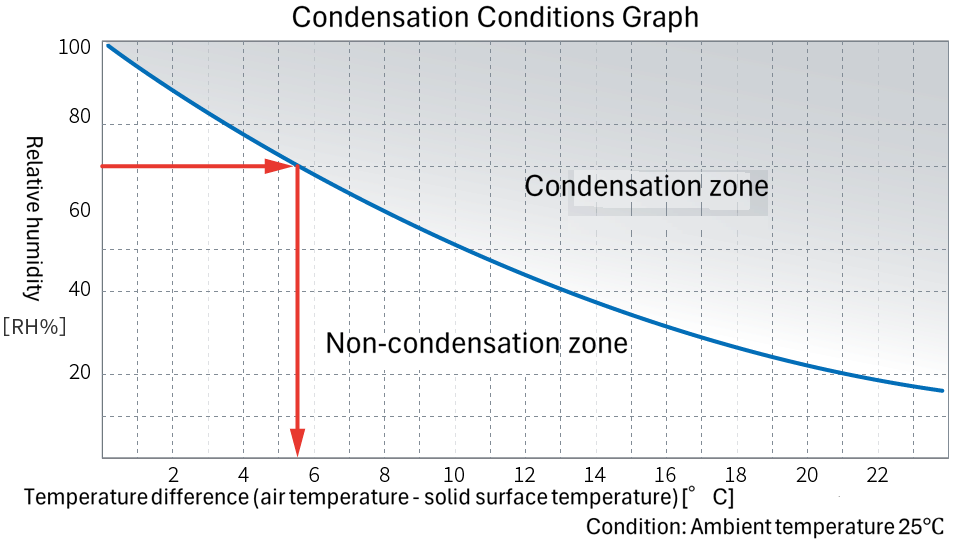
Condensation occurrence conditions characteristics

Use a control panel cooling unit to make the internal board environment the best condition it can be!
control panel cooling unit protect electronic devices inside panel from heat, dust, and humidity, contributing to the stable operation of production lines.
Please check the catalog for the latest lineup, functions and features.






